

Even if it’s not required, a balance sheet gives you the information you need to fill out forms accurately and avoid costly mistakes. If assets are greater than liabilities, the company has a positive net financial position, indicating a stronger financial position. However, if liabilities are greater than assets, the company has a negative net financial position, which may indicate financial problems. Companies make their shares available for public trading to provide capital that can be used easily.
- Holders of common stock elect the corporation’s directors and share in the distribution of profits of the company via dividends.
- While the financial statements are closely intertwined and necessary to understand a company’s financial health, the balance sheet is particularly useful for ratio analysis.
- A visual aid used by accountants to illustrate a journal entry’s effect on the general ledger accounts.
- It helps you understand where you stand financially and what you can do next.
- In the Balance Sheet, Assets are reported in the first part before Equity and Liabilities.
- You can improve your current ratio by either increasing your assets or decreasing your liabilities.
- If the company takes $8,000 from investors, its assets will increase by that amount, as will its shareholder equity.
Steps in Long-Term Financial Planning: A Strategic Roadmap…
All of our business forms contain an Excel template, a blank PDF form, and a filled-in PDF form. Understanding what a balance sheet can tell you will help you in investing and making informed financial decisions. A company’s balance sheet will tell you if it is in a stable financial condition or struggling with debt. Based on other factors about the company, you can determine whether it’s a good investment or if you might lose your money. With a greater understanding of a balance sheet and how it is constructed, we can review some techniques used to analyze the information contained within a balance sheet. It is important to note that a balance sheet is just a snapshot of the company’s financial position at a single point in time.
Financial Planning Cycle: What It Is and Why…
- This is especially helpful in understanding the stockholders’ equity section.
- The information stated on the balance sheet is as of the end of a reporting period.
- Until the company delivers the services or goods, the company has an obligation to deliver them or to refund the customer’s money.
- Enter the details of your current fixed and long-term assets and your current and long-term liabilities.
- Since the gain is outside of the main activity of a business, it is reported as a nonoperating or other revenue on the company’s income statement.
- The additional column allows the reader to see how the most recent amounts have changed from an earlier date.
Here, the equities and liabilities are at the top, while the assets are at the bottom. It is the difference between a firm’s total assets and its total liabilities. The result shows how fruitful the investment could be for investors, indicating the potential for the returns to multiply in the future. Accordingly, they decide whether to invest, reinvest, or withdraw their financial backing.
how detailed can balance sheets be?
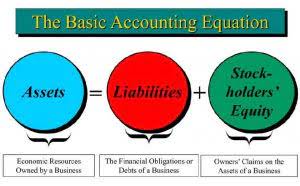
While the financial statements are closely intertwined and necessary to understand a company’s financial health, the balance sheet is particularly useful for ratio analysis. The fundamental accounting equation states that a company’s assets must be equal to the sum of its liabilities and shareholders’ equity. In simple terms, the balance sheet—also known as the “statement of financial position”—provides a comprehensive overview of a company’s assets (“what is owned”) and liabilities (“what is owed”) in a given period. The Balance Sheet—or Statement of Financial Position—is a core financial statement that reports a snapshot of a company’s assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity at a particular point in time. The balance sheet shows the financial position of the company at a particular point in time.
The Need to Understand the Statement of Financial Position
A company can use its balance sheet to craft internal decisions, although the information presented is usually not as helpful as an income statement. A company may look at its balance sheet to measure risk, make sure it has enough cash on hand, and evaluate how it wants to raise more capital (through debt or equity). Public companies, on the other hand, are required to obtain external audits by public accountants and must also ensure that their books are kept to a much higher standard. Shareholder equity is the money attributable to the owners of a business or its shareholders. It is also known as net assets, as it represents the total assets of a https://www.bookstime.com/ company minus its liabilities, or the debt it owes to non-shareholders.

Repairs expense
Inventory contributes to COGS (cost of goods sold) and is valued using either the First In First Out (FIFO) or Last In Last Out method. Again, these accounting balance sheet are classed as assets and can be sold off in a liquidity event. Bill’s quick ratio is pretty dire—he’s well short of paying off his liabilities with cash and cash equivalents, leaving him in a bind if he needs to take care of that debt ASAP. He doesn’t have a lot of liabilities compared to his assets, and all of them are short-term liabilities. You can improve your current ratio by either increasing your assets or decreasing your liabilities.

Profit and Loss (P&L) Statement

To illustrate, assume that a distributor spends $200,000 to buy goods for its inventory. If it takes 3 months to sell the goods on credit and then another month to collect the receivables, the distributor’s operating cycle is 4 months. Because one year is longer than the 4-month operating cycle, the distributor’s current assets includes its cash and assets that are expected to turn to cash within one year. Typically, the balance sheet date is the final day of the accounting period. If a company issues monthly financial statements, the date will be the final day of each month. The balance sheet is one in a set of five financial statements distributed by a U.S. corporation.
- For example, the assets, particular the long term assets are normally shown at cost or revaluation at a point in time, they do not show the current market value of those assets.
- Cash is considered the most liquid of all assets, but other short-term assets include items like accounts receivable and prepaid rent or prepaid insurance..
- However, there are several “buckets” and line items that are almost always included in common balance sheets.
- Liabilities represent the obligations a company owes to external parties.
Short-term loans payable
The long-term asset construction in progress accumulates a company’s costs of constructing new buildings, additions, equipment, etc. Each project’s costs are accumulated separately and will be transferred to the appropriate property, plant, or equipment account when the asset is placed into service. Inventory is likely the largest Payroll Taxes current asset on a retailer’s or manufacturer’s balance sheet. The reported amount on the retailer’s balance sheet is the cost of merchandise that was purchased, but not yet sold to customers. Generally, a company’s accounts receivable will turn to cash within a month or two depending on the company’s credit terms. The balance sheet item accounts receivable – net (or trade receivables – net) is the amount in the company’s account Accounts Receivable minus the amount in the contra account Allowance for Doubtful Accounts.